|
3/10/2017 0 Comments Extract Psx Iso From BooterI was able to extract files from a personal 'back up' DVD that had not closed properly so I could not open it with any dvd player/burner. How to Boot Linux ISO Images Directly From Your Hard Drive. Linux’s GRUB2 boot loader can boot Linux ISO files directly from your hard drive. Boot Linux live CDs or even install Linux on another hard drive partition without burning it to disc or booting from a USB drive. We performed this process on Ubuntu 1. Ubuntu and Ubuntu- based Linux distributions have good support for this. Other Linux distributions should work similarly. Get a Linux ISO File. This trick requires you have a Linux system installed on your hard drive. Your computer must be using the GRUB2 boot loader, which is a standard boot loader on most Linux systems. 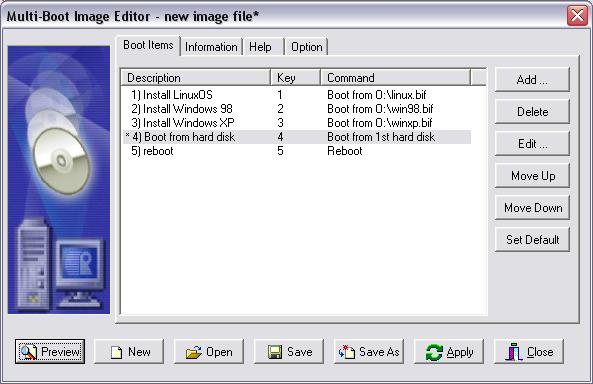
Sorry, you can’t boot a Linux ISO file directly from a Windows system using the Windows boot loader. Download the ISO files you want to use and store them on your Linux partition. GRUB2 should support most Linux systems. Many Linux- based bootable utility discs should also work. Check the Contents of the ISO File.

You may need to look inside the ISO file to determine exactly where specific files are. For example, you can do this by opening the ISO file with the Archive Manager/File Roller graphical application that comes with Ubuntu and other GNOME- based desktop environments. In the Nautilus file manager, right- click the ISO file and select Open with Archive Manager. Locate the kernel file and the initrd image. If you’re using a Ubuntu ISO file, you’ll find these files inside the casper folder — the vmlinuz file is the Linux kernel and the initrd file is the initrd image. You’ll need to know their location inside the ISO file later. Determine the Hard Drive Partition’s Path. GRUB uses a different “device name” scheme than Linux does. On a Linux system, /dev/sda. I'm trying to extract files from an.IMG file of a PSX game. I would imagine this is similar to ISO, however. Extract, edit, rename ISO files directly. We had been using WinISO for 2 years to create ISO or Extract files we want to save. WinISO is a powerful ISO Extractor, which can extract not only ISO image file but extract any other file formats if you desired. INTERNATIONAL: Jp De En. In GRUB, (hd. 0,1) is equivalent to /dev/sda. The 0 means the first hard disk, while the 1 means the first partition on it. In other words, in a GRUB device name, the disk numbers start counting at 0 and the partition num. For example, (hd. You can use the fdisk - l command to view this information. On Ubuntu, open a Terminal and run the following command: sudo fdisk - l. You’ll see a list of Linux device paths, which you can convert to GRUB device names on your own. 
For example, below we can see the system partition is /dev/sda. GRUB. Create the GRUB2 Boot Entry. 
The easiest way to add a custom boot entry is to edit the /etc/grub. This file is designed for user- added custom boot entries. After editing the file, the contents of your /etc/defaults/grub file and the /etc/grub. It’s designed to be automatically generated from settings you specify in other files. 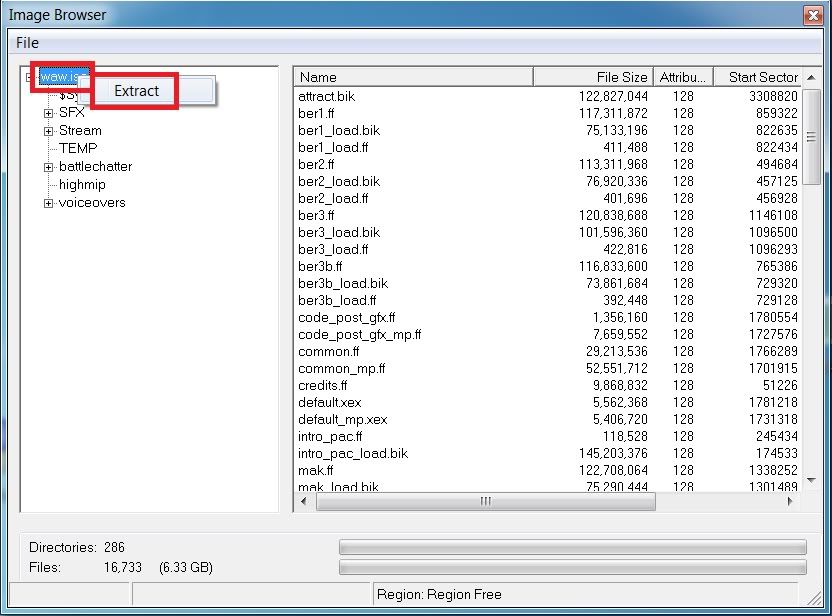 
You’ll need to open the /etc/grub. On Ubuntu, you can do this by opening a Terminal window and running the following command: sudo gedit /etc/grub. For example, you could replace “gedit” with “nano” in the command to open the file in the Nano text editor. Unless you’ve added other custom boot entries, you should see a mostly empty file. You’ll need to add one or more ISO- booting sections to the file below the commented lines. Here’s how you can boot an Ubuntu or Ubuntu- based distribution from an ISO file. We tested this with Ubuntu 1. Ubuntu 1. 4. 0. 4 ISO” . If the vmlinuz and initrd files have different names or paths, be sure to specify the correct path to those files, too.(If you have a separate /home/ partition, omit the /home bit, like so: set isofile=”/name/Downloads/$. The GRUB Live ISO Multiboot project offers a variety of menu entries for different Linux distributions. You should be able to adapt these example menu entries for the ISO file you want to boot. You can also just perform a web search for the name and release number of the Linux distribution you want to boot along with “boot from ISO in GRUB” to find more information. If you want to add more ISO boot options, add additional sections to the file. Save the file when you’re done. Return to a Terminal window and run the following command: sudo update- grub. The next time you boot your computer, you’ll see the ISO boot entry and you can choose it to boot the ISO file. You may have to hold Shift while booting to see the GRUB menu. If you see an error message or a black screen when you attempt to boot the ISO file, you misconfigured the boot entry somehow. Even if you got the ISO file path and device name right, the paths to the vmlinuz and intird files on the ISO file may not be correct or the Linux system you’re booting may require different options.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorWrite something about yourself. No need to be fancy, just an overview. ArchivesCategories |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
